No products in the cart.

CBD 101
What is CBD?
CBD is one of more than 80 active cannabinoid chemicals in hemp plants. Unlike its well-known sibling, THC, CBD is not psychoactive.
The Endocannabinoid System
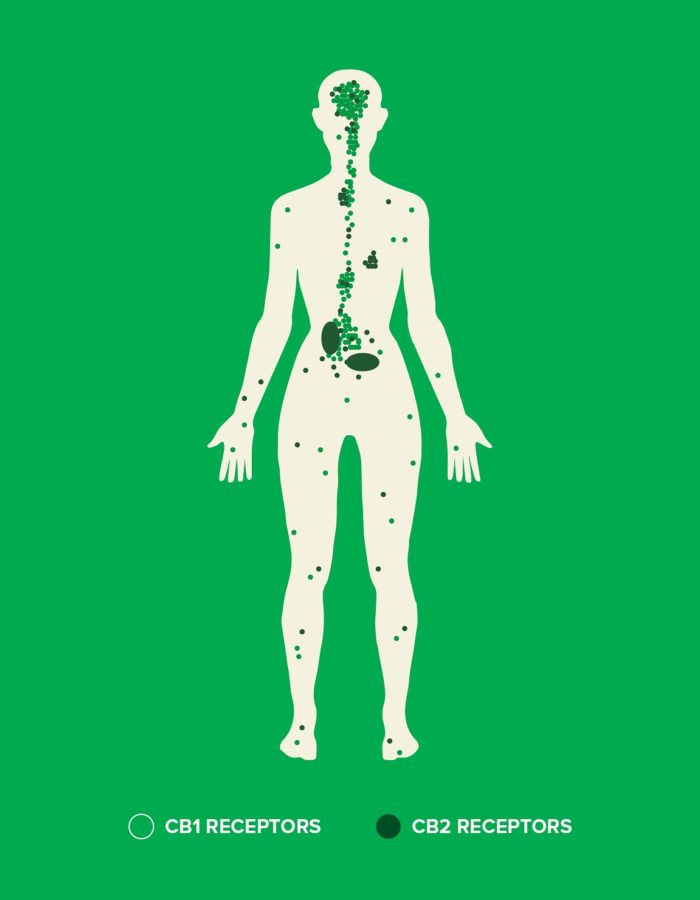
CBD acts as stimuli for the cannabinoid receptors in the brain, gut, and immune system to support mental and physical health. Ingesting this potent antioxidant also activates the endocannabinoid system (ECS) located in the brain and throughout the central nervous system. The ECS is perhaps one of the most valuable biological systems supporting you from day-to-day. It is primarily made of neuromodulatory lipids and their receptors, which are found in various tissues throughout the body. In each tissue, cannabinoids perform different tasks to maintain your body’s delicate balance through the ups and downs of life.
The ECS contains two main types of receptors, cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid 2 (CB2). These receptors help balance and support the following: healthy heart, muscles, joints, bone health, a sense of calm, and daily stresses.

Difference Between Hemp and Marijuana
While hemp and marijuana look and smell the same, they are both very different plants. Marijuana contains THC, a molecule that binds itself to the receptors in the brain and is responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis. Hemp, in comparison, contains non-psychoactive CBD that attaches itself to endocannabinoid receptors throughout the rest of the body but does not give you a high.
History of Hemp
Originating from 8000 BC, hemp stems from a strain of the Cannabis sativa plant that is not psychoactive. Since then, people have used hemp in thousands of ways, from cloth to paper to apothecary remedies. The 2018 Farm bill legalized the production of hemp as an agricultural commodity while removing it from the list of controlled substances.

